Nursing Presentation/ History of Nursing
Table of Contents
Summary of Ancient Cultures
Introduction:
Ancient Egypt is considered as one of the earliest, longest-lasting and most prominent civilization in history.
Ancient Egyptians overlapped between magic, religion, sin, punishment, and the influence of the supernatural in the events of daily life.
Demons and Sins were assumed to bring diseases, sickness and disabilities as way of punishment.
In ancient Egypt, health care professions such as physician or healers were usually priests who were accountable for healing physical and psychological
diseases.
The priests acted as a link between humans and gods. They believed that people had to make the Gods happy to have good health and peace of mind.
The embalmer is the one who prepares the mummies to keep the body after death without damage because to improve their knowledge of anatomy comparing the anatomy of human bodies with that of animal bodies as indicated in the most of their ancient texts’
Other fields with such as the pharmacist, bandagers, masseur and even amulet seller who was trained to take the pulse
Medical treatment In ancient Egypt:
Ancient Egypt treatment includes leaves, grass and the bark of the willow tree contain salicylic acid used to treat inflammatory disease, to alleviate birth pains and reduce fever.
Egyptian doctors could stitch up wounds, repair broken bones and amputate infected limbs. The incision was dressed by mixture of raw meat, linen, and swabs soaked with honey. At the beginning of the Late period and early Ptolemaic period [656 BC–323 BC], the so-called healing statues were appeared.
Internal disorders were managed by using magic and amulets in this case will be wider beside the invocations to gods who were considered to be involved in both causing diseases and cure them.
Different title to Caregivers In Ancient Egypt:
The Coffin Texts were developed in the first Intermediate Period [2134 BCE–2040 BCE] and composed of the Pyramid Texts, which had been placed only in royal tombs/ pyramids) Also, for the first time the male title ”male nurse“ was attested in the (CT) as a God’s child or as priestly title.

Site of Healthcare in Ancient Cultures:
According to the Ottawa Charter, ‘Health Promotion’ is a health strategy that aims to incorporate skills and community development and to create supportive environments for health, endeavors to build healthy public policy and looks at re-orienting health services (WHO, 1986).
Although it is commonly accepted that these basic concepts of health promotion have been developed in the last two decades, they have roots in ancient civilizations and in particular in Greek antiquity.
As evident from medical and philosophical documents—especially of the sixth to fourth centuries B.C. the ancient Greeks were the first to break with the metaphysical/supernatural conceptions of health and disease that had so far dominated human societies (Edelstein, 1987).
The ancient Greeks’ apprehension of health and illness was based on the theory of the four ‘fluids’ (blood, phlegm, yellow bile and black bile) which was of great significance for Pythagorean philosophy that dominated the pre-Socratic period (Temkin, 1995).
Hippocratic:

Pathogenic process, according to Hippocratics, is a result of the overturn of equilibrium and the predominance of one of the four fluids that causes disease through the disruption of the equilibrium of the four fluids
Hippocratics posited a natural theory of disease etiology and notes that the treatment of male impotence.
Hippocratics recognized that some diseases were always present in a given population. They called these diseases ‘endemic’, whereas other diseases, which were not always present but which occurred in greater frequency at certain times, they called ‘epidemic’. Both terms are widely used today. Rosen (1993)
Hippocrates’ treatise About Wind, Water and Places is not only a text of great historical value but also a groundbreaking achievement. Beneficence and nonmaleficence are age old requirements of the Hippocratic Oath for health professionals to ‘do good’ and ‘do not harm’ (Racher, 2007).
Greek History:
Little is known of Greek medicine before the appearance of written texts in the fifth century B.C. Greece as many other prehistoric countries possessed folk healers, including priest healers and chief tribunes employing divination and drugs.
Greek society at large drew heavily upon sacred healing. In Homer, Apollo appears as the ‘God of healing’.
Once Asklepius was recognized as the God of medicine.
During the fourth and the third century the cult of Asclepius and the practice of Hippocratic medicine spread, and by 200 B.C. every large town in Greece had an Asklepieion.
Roman Empire:
- After 300 BC they built them self with the work of Greece and Egyptian.
- They advance their work more and known as best in public health.
- Believe health can be restored by God.
- Two classes Patricians (upper class) and Plebicians (Lower class).
- Organized group and funded monasteries and hospitals.
India:
- They mostly hired male staff for work
- They work on four major components knowledge, devotedness, cleverness and purity.
- First civilizations were highly developed 1500 BC.
- The first master’s degree course, two year postgraduate program was begun in 1960 at college of nursing Delhi.
Christianity:
Women begin nursing as an expression of Christianity( Act of mercy) ,Christianity brings the clear role of Nursing in modified way. Women work in care of sick people and male contribute themselves in to buried the dead people. Fabiola started the first public hospital in Rome.
Middle Ages:

Established the first educational program to be affiliated with a religious nursing order with care provided by monks and nuns.
More hospital were built and Nursing role became more prominent.
The Eastern Orthodox Church had established many hospitals in the middle east.
Nursing care was controlled by catholic church.
Known as Dark Ages – intellectual progress nearly halted.
Fifteenth to Nineteenth Century:
The Eastern Orthodox Church had established many hospitals in the middle east, but following the rise of Islam from the 7th century. Increased in population in cites with more hygiene and sanitation leads to sever health problems. Society changes were forming a great effect on health care system.
Nursing in Mughal period:
- Emperor Akbar went through many vicissitudes in his life and probably the most cumbersome was the presence and activities of his wet-nurse or foster mothers known in the Mughal world as ‘angas’.
- Maham Anaga was the governess of Emperor Akbar. As the word ‘Anaga’ means nurse.
- Maham Anga (died 1562) was the chief nurse of the Mughal emperor Akbar from 1560 to 1562.
Islam and Nursing:
Islamic traditions include sympathy for and responsibility toward those in need. Rufaida Al- Aslamia introduced nursing in Muslim world 1’200 Years before. Rufaida Al- Aslamia was recognized for her work in medical and social circle. She was the first female Muslin Nurse. She was among first people in Madinah to accept Islam. She contributed with other Ansar women to welcome Muhammad ( peace be upon him) on arrival in Madinah.
Pre-Islamic and Islamic Era (570–632 AD):
Rufiada Al- Aslamia’s father, Saad Al- Aslami, was a physician and mentor. She initially obtained clinical experience from her father. Then deovoted herself to nursing. she practiced her skills in field hospital in her tent during many battles.
When Saad Ibn Muaath was injured in the battle of Al-Khandaq ( The Trench) , Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) ordered that he be placed and treated in her tent.
She focused on hygiene and stabilizing patients prior further more invasive medical procedures.
Rufaida led groups of volunteer nurses who went to battlefield and treated the casualties. She participated in the battles of Badr, Uhud, Khandaq, khaibar and others.
The founder of Modern Nursing:
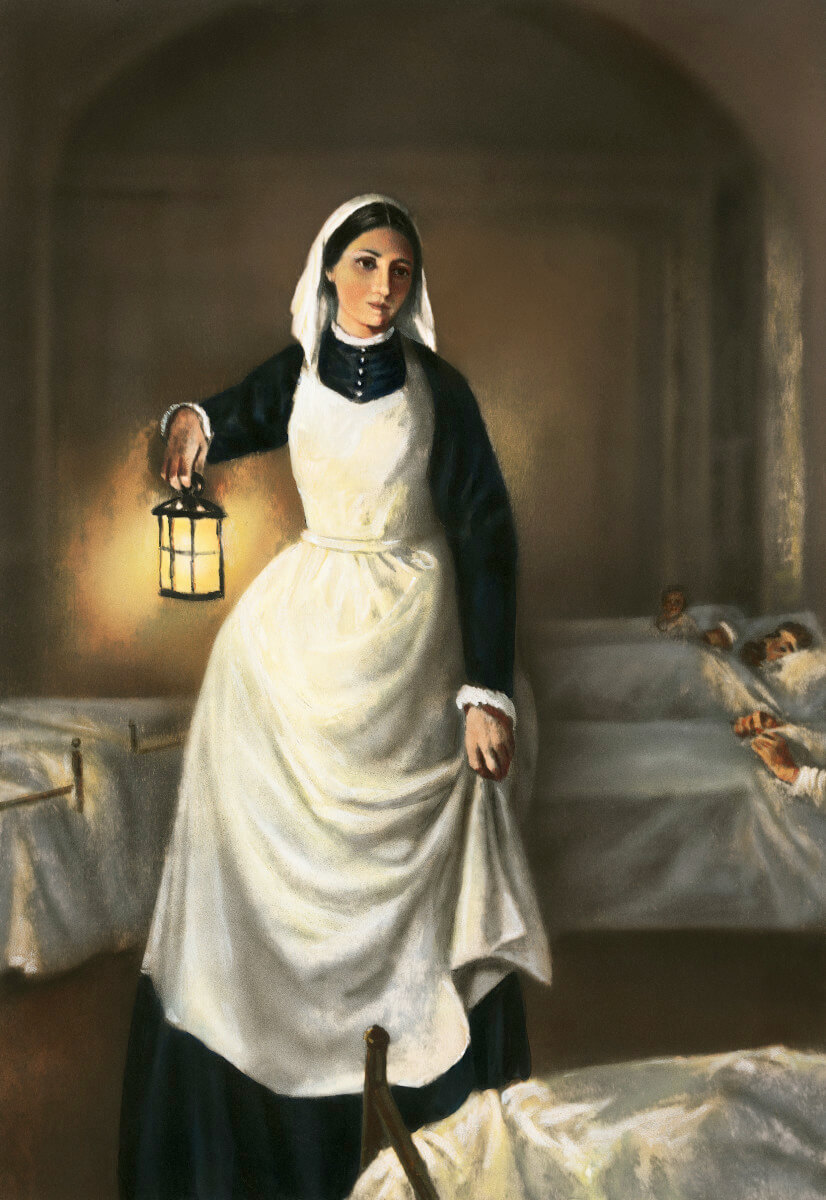

- Florence Nightingale (May 12, 1820 – August 13, 1910)
- She was English reformer, statistician and the founder of modern nursing.
- Nightingale came to prominence while serving as a manager and trainer of nurses during the Crimean War , in which she organized care for wounded soldiers at Constantinople.
- She became Icon of Victorian culture by giving nursing favorable reputation.
The Lady with the Lamp:
She is also refer as “The Lady with the Lamp” . In 1860, she laid the foundation of professional nursing with the establishment of her nursing school at St Thomas’ Hospital London. It was the first secular nursing school in the world. Annual International Nurses Day is celebrated on her birthday
Definitions of Nursing:
Definition of Nursing by WHO:
Nursing encompasses autonomous and collaborative care of individuals of all ages, families, groups, and communities, sick or well, and in all settings. It includes the promotion of health, the prevention of illness, and the care of ill, disabled, and dying people.
Definition of nursing by Virginia Henderson:
“The unique function of the nurse is to assist the individual, sick or well, in the performance of those activities contributing to health or its recovery (or to peaceful death) that he would perform unaided if he had the necessary strength, will or knowledge“\
Definition of Nursing by Florence Nightingale:
Nursing is a profession within the health care sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life.
Definition of nursing by Dorothea Orem:
The self-care deficit nursing theory is a grand nursing theory that was developed between 1959 and 2001 by Dorothea Orem. The theory is also referred to as the Orem’s Model of Nursing.
Definition of Nursing by Effie Taylor:
“The adaptation of the prescribed therapeutic and preventive treatment for physical and psychological needs specific person“.
Nursing Defined by International Council of Nursing:
Nursing encompasses autonomous and collaborative care of individuals of all ages, families, groups and communities, sick or well and in all settings.
Nursing includes the promotion of health, prevention of illness, and the care of ill, disabled and dying people.
Definition of nursing by ANA (American Nurses Association):
Nursing is the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and abilities, prevention of illness and injury, facilitation of healing, alleviation of suffering through the diagnosis and treatment of human response, and advocacy in the care of individuals, families, groups, communities, and populations.
Types of Nursing Educational Programs:
- Nursing Diploma and associated degree in nursing (AND) program
- Bachelor of science in nursing (BSN) program
- Master of science in nursing (MSN) program
- Family Nurses practitioner (FNP) program
- Midwifery program
- Doctor of nursing practice (DNP) and Ph.D
Resources:
Elhabashy, Sameh & Abdelgawad, Elshaimaa. (2019). The History of Nursing Profession in Ancient Egyptian Society. International Journal of Africa Nursing Sciences. 11. 100174. 10.1016/j.ijans.2019.100174.
Frenk, Julio, Lincoln Chen, Zulfiqar A. Bhutta, Jordan Cohen, Nigel Crisp, Timothy Evans, Harvey Fineberg, et al. (2010). Health professionals for a new century: transforming education to strengthen health systems in an interdependent world. The Lancet 376(9756): 1923-1958.
Alligood MR, Tomey AM. Nursing Theorists and Their Work. 6th ed. Mosby: Singapore; 2006. [Google Scholar]

Pingback: Unit 2 Roles of Nurse in Health Care
That’s true.